Publication: Investigating Zinc Migration from Rigid Needle Shield to Drug Formulation in Needle Tip of Pre‑filled Syringe
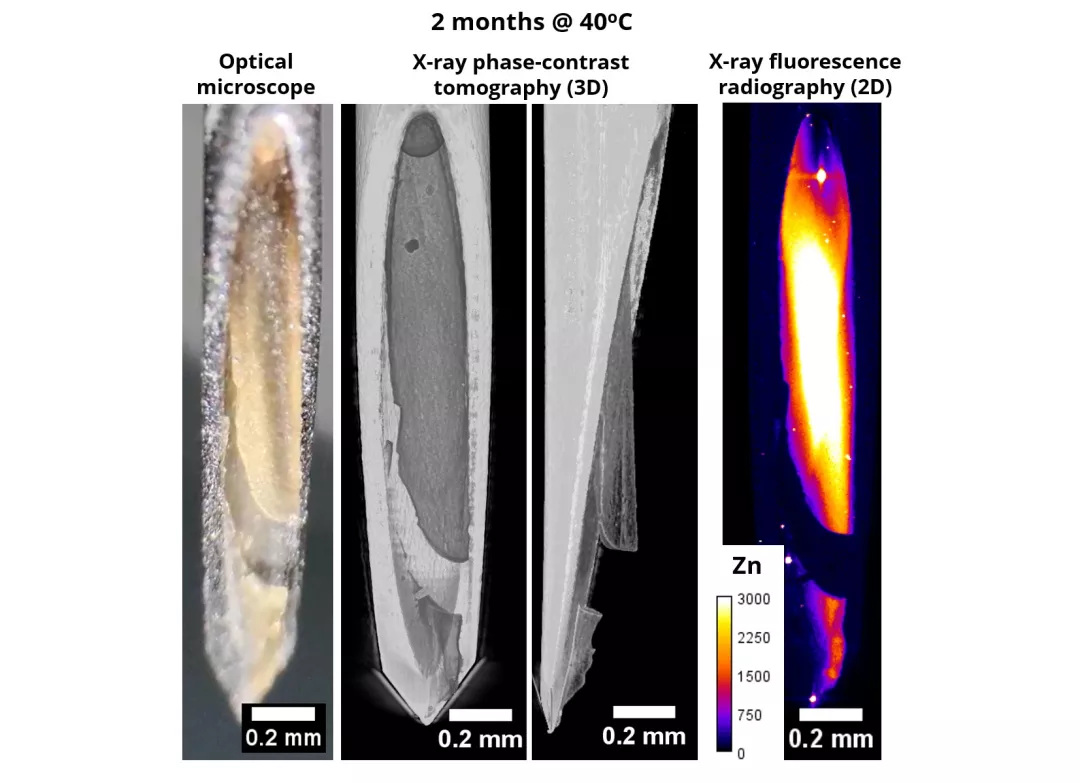
Pre-filled syringes containing a therapeutic monoclonal antibody were stored at 5 °C and subjected to stress conditions at 40 °C for up to six months. Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) was used to measure metal ion levels, while synchrotron-based X-ray phase-contrast computed tomography and X-ray fluorescence enabled in situ visualization of Zn distribution in dry materials under stress.
The study found that Zn leaches from the rigid needle shield (RNS) into the drug formulation during liquid–RNS contact. This work provides the first experimental evidence of Zn migration from the RNS into drug formulations within staked-in-needle pre-filled syringes (PFSs).
While Zn is not solely responsible for needle clogging, its presence in both the RNS and the drug formulation suggests a contributory role. These insights can inform strategies to improve PFS performance and reliability.
Link to publication: Link