Small-Angle Scattering
Neutron and Synchrotron Small-Angle Scattering – Two complementary methods for providing structural information
Your benefits compared to lab-based analytics
The materials that make up an industrial product often go through complicated processes before they reach their final shape and form. Every process that has been performed influences the final structure, and therefore the properties, of the product. Diffraction and Small-Angle Scattering are methods available for detecting phases and their morphologies.
Synchrotron techniques provide high transmission with light elements, and strong contrast with heavier elements. Neutron techniques, on the other hand, provide strong contrast with light elements, and higher transmission with heavier elements. This means that the two methods offer different yet complementary contrast possibilities.
Small-Angle Scattering can be used for morphological characterization, such as the size, shape and orientation distributions of different kinds of materials.
Neutron and Synchrotron techniques deliver high resolution, high throughput, and allow real-time investigations. The data obtained provides the basis for further analytical capabilities, as described below.
We are looking forward to working with you.
Small-Angle Scattering is used as a qualitative and quantitative measurement technology with the following analysis capabilities:
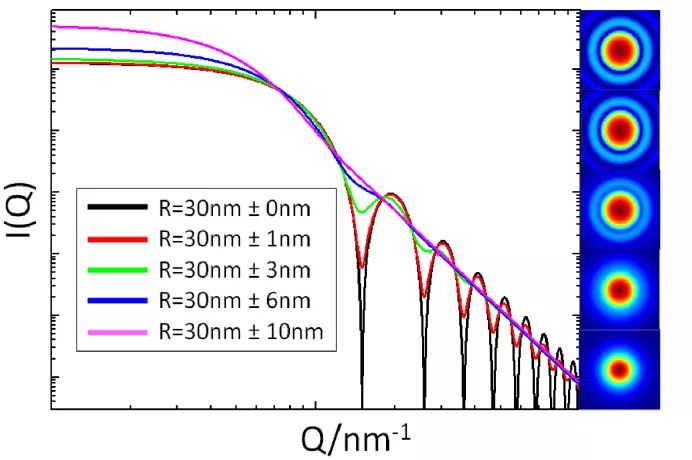
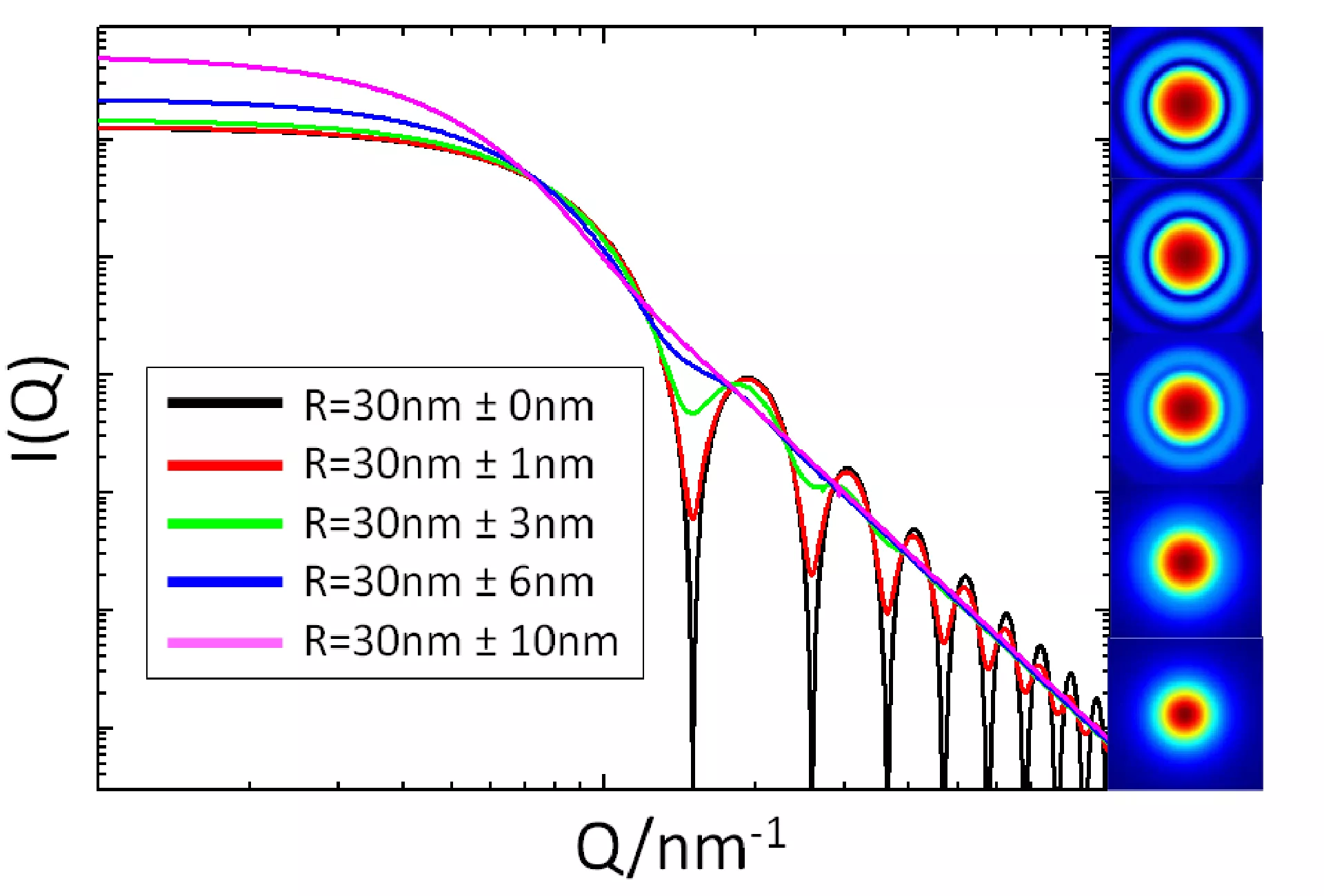
Size distribution analysis
- Determination of the nano- and micro-scale structures of randomly oriented systems
- Quantification of particle size distribution of poly-dispersed systems
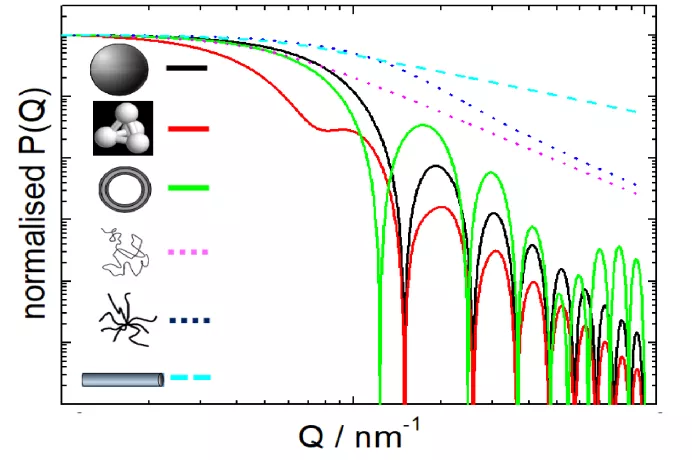
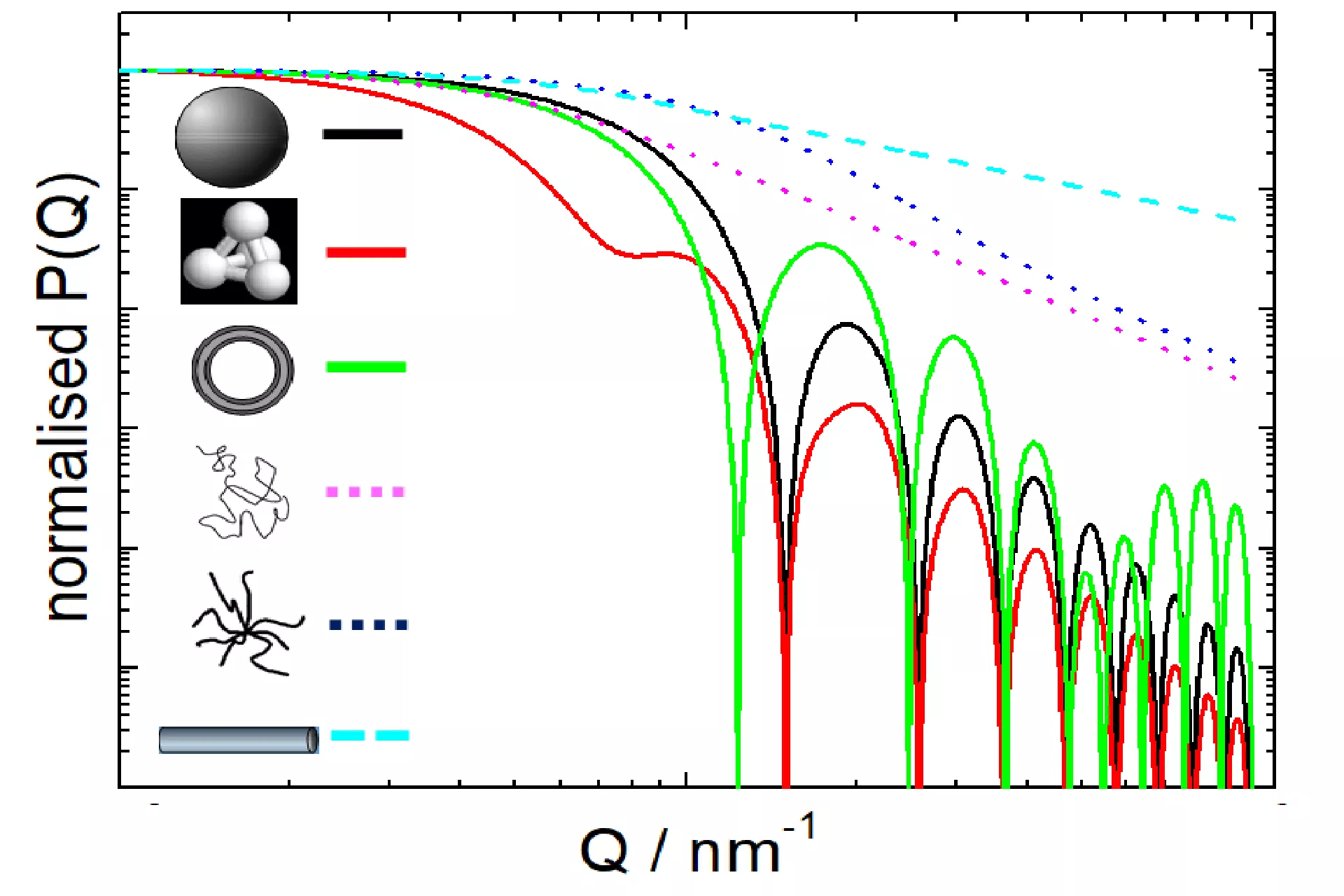
Shape distribution analysis
- Identification of external form and internal structures
- Determination of shape distributions
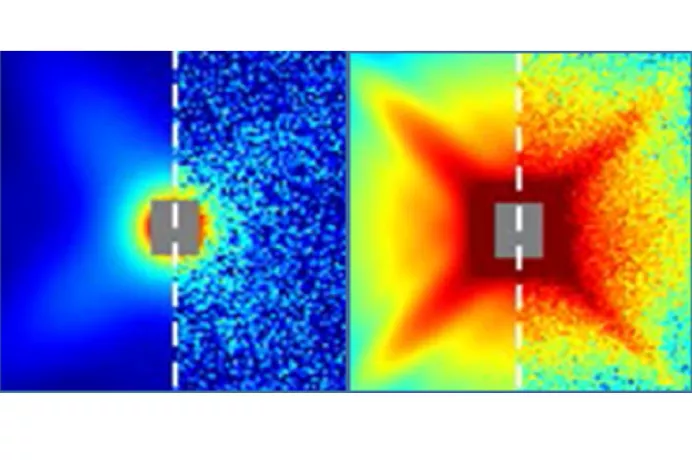
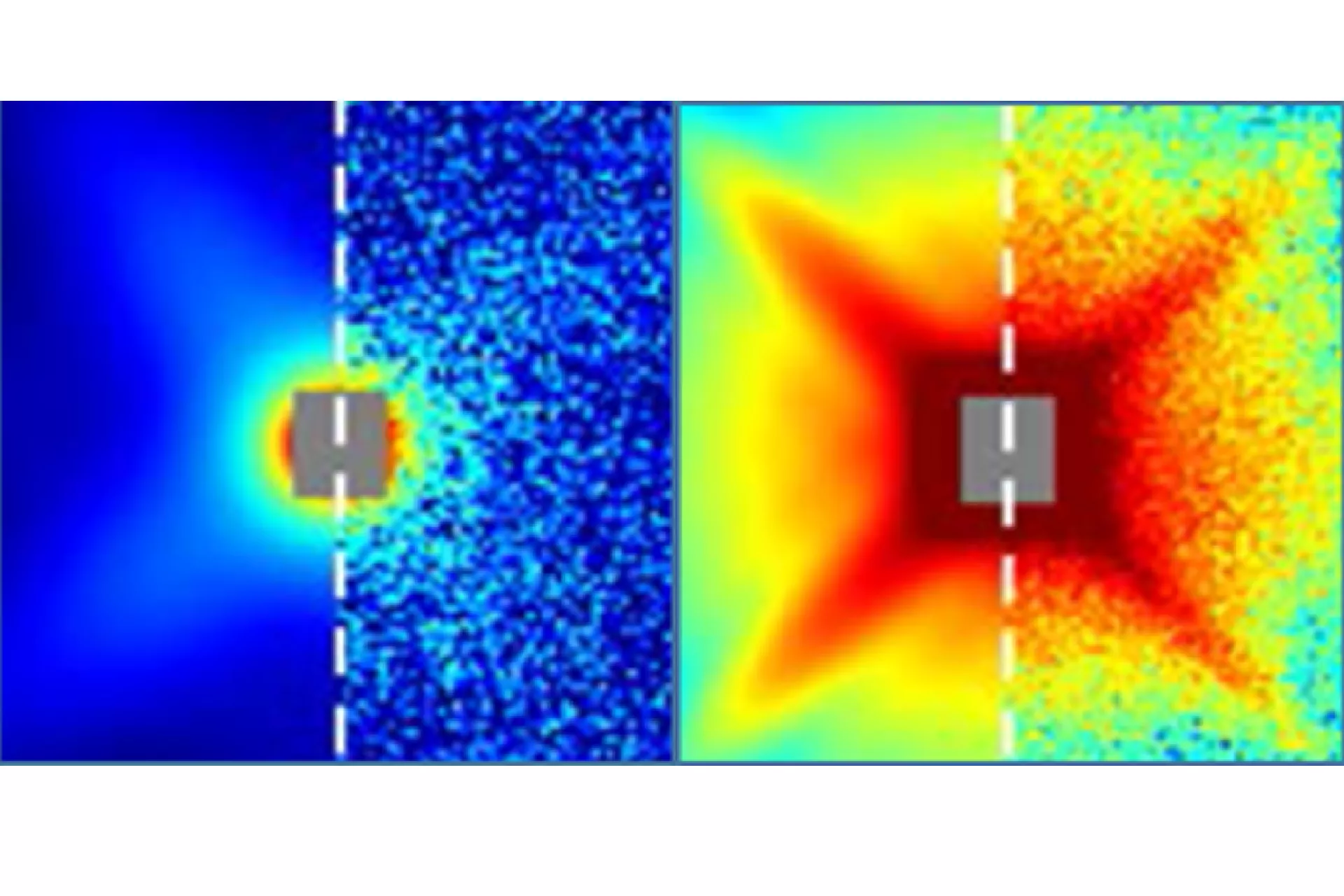
Orientation analysis
- Determination of alignment of structures
We’re here to help
Industrial challenges can be highly specific. We’d be happy to discuss your individual case in detail. Schedule a meeting with us to learn how we can contribute to finding the right solution.
The complementarity of Neutron and Synchrotron Small-Angle Scattering
Selection of advantages of each technique
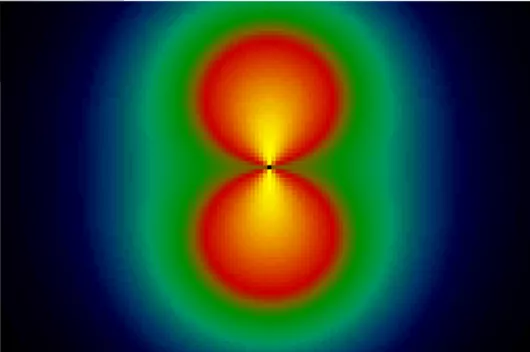
Neutron Small-Angle Scattering
- Higher contrast for light elements (such as H, B, Li)
- Higher penetration of metallic elements (such as Ti, Cr, Fe)
- Higher contrast difference for neighboring elements (as example Pd and Rh)
- Sensitive to magnetic structures
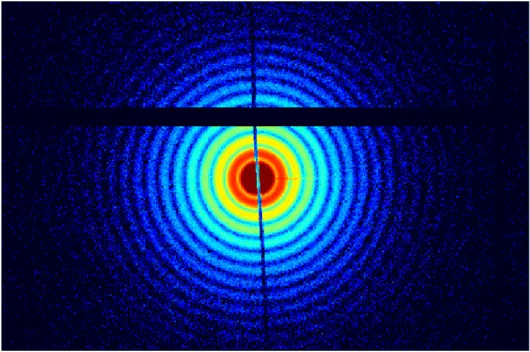
Synchrotron Small-Angle Scattering
- Higher penetration for light elements (such as H, B, Li)
- Higher contrast for of metallic (such as Ti, Cr, Fe)
- Higher spatial resolution compared to neutrons and lab-based X-ray systems
- Much higher temporal resolution compared to neutrons and lab-based X-ray systems
- Much higher sample throughput compared to neutrons and lab-based X-ray systems
Technical details of Neutron and Synchrotron Small-Angle Scattering
Selection of detailed information
| Information | Neutron
Small-Angle Scattering |
Synchrotron
Small-Angle Scattering |
|---|---|---|
| Energy range |
0.05 - 4 meV |
2.8 - 41.3 keV |
|
Wavelength |
4.5 - 40 Å |
0.3 - 4.4 Å |
|
Sample to detector distance |
1 - 18 m |
2.1 - 7.2 m |
|
Accessible q-range |
0.0006 - 1.5 Å-1 |
0.0012 - 2.81.5 Å-1 |
| Resolution |
Δλ/λ = 10 % |
ΔE/E = 0.02 % |
| Spot Size | Up to 2.5 x 2.5 mm2 maximum | Down to 25 x 10 µm2 minimum |
The way we work with you
Your
challenge
Competent
consulting
Applied material analytics with Neutron and Synchrotron radiation &
tailor-made infrastructure
Data analysis and interpretation
Final
report
Our specialized tools for your specific challenges
This is how we analyze your challenges – making the invisible visible: precise, reliable, and reproducible.
Open the drawers and learn more:






Sample preparation and pre- /post- characterization
Move your mouse over the drawers to explore our tools for applied material analytics.
Click the drawers to learn more
Tap the drawers to learn more