Imaging
How is imaging used in industrial applications?
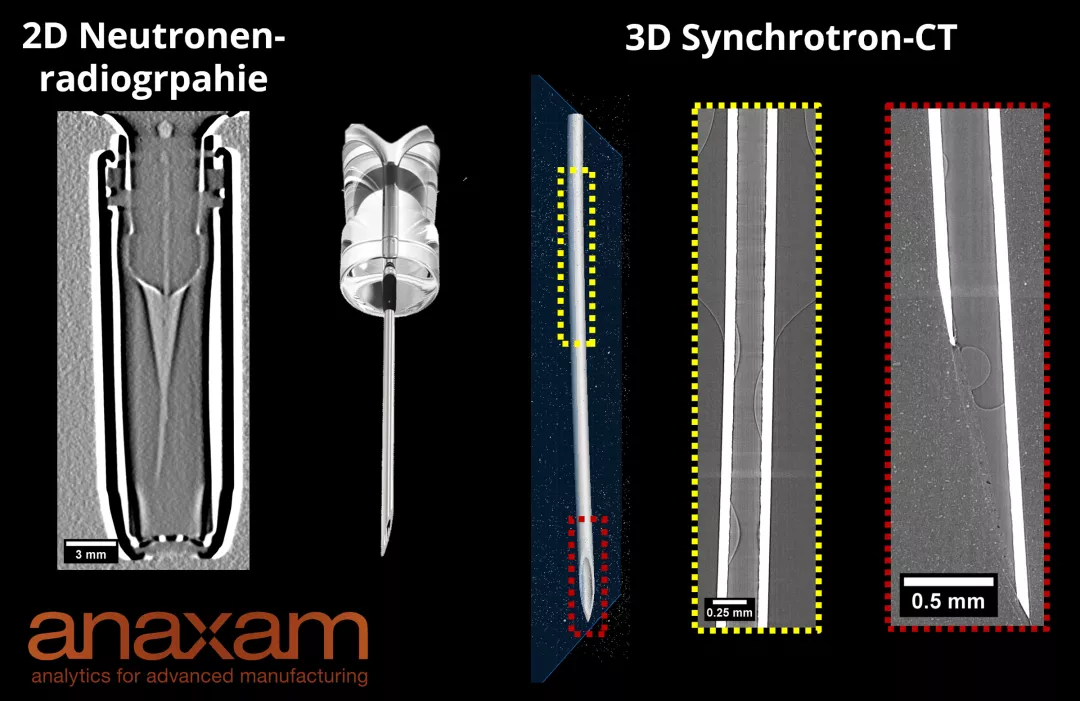
Imaging refers to methods that generate visual representations of objects based on physical parameters such as light, sound, or electromagnetic radiation. These techniques are especially valuable in industry because they allow non-invasive analysis. One key application area is material inspection, where 3D computed tomography is used to visualize internal structures, analyze material distributions, identify defects and porosity, measure wall thickness, and perform actual-to-target comparisons. Synchrotron and neutron CT offer varying levels of contrast and are suitable for examining different types of materials. Reverse engineering also relies on imaging to reconstruct detailed 3D models of objects without original designs, supporting further research and development processes.
Added Value and Benefits
- Non-destructive testing: Objects do not need to be cut or damaged to examine internal structures.
- High resolution and accuracy: Cutting-edge technologies such as synchrotron CT deliver detailed, high-resolution images for precise analysis.
- Time and cost efficiency: Fast scans and direct access to digital data reduce the need for physical prototypes and repeated testing.
- Versatile applicability: Suitable for various fields including materials science, biology, archaeology, and more.
- Supports product development: Enables optimization of products and processes through detailed insights into material behavior and manufacturing defects.
Questions and Answers (FAQ)
- Can imaging be used for very small or very large objects?
Yes, imaging techniques are scalable and can be applied to objects of various sizes—from microscopic samples to large industrial components.
- Are imaging methods limited to specific types of materials?
No, techniques such as X-ray CT, synchrotron CT, and neutron CT allow the examination of a wide variety of materials with different properties.
- How accurate is the data obtained through imaging techniques?
Accuracy can be very high, depending on the technology used and the resolution of the scanner.
- Can imaging be performed in real time?
Yes, both X-ray and neutron imaging can be used to study dynamic processes in real time.
- Can companies use imaging for product and process development?
Absolutely. These techniques are ideal for product development and quality control, especially in complex and technically demanding areas.
Contact
Interested in gaining deeper insights into your materials? Contact ANAXAM for a no-obligation consultation. Learn how our imaging analytics can help you reach your research and development goals.
Further key terms
3D scanning, computed tomography, material analysis, defect analysis, reverse engineering, synchrotron CT, neutron CT, industrial tomography, non-destructive testing (NDT)