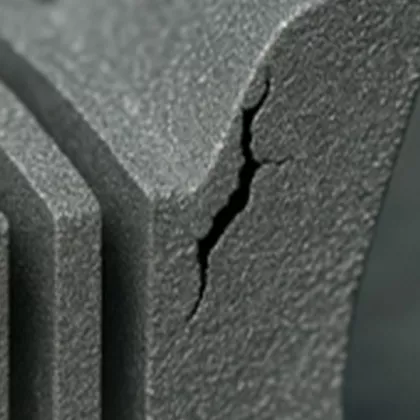
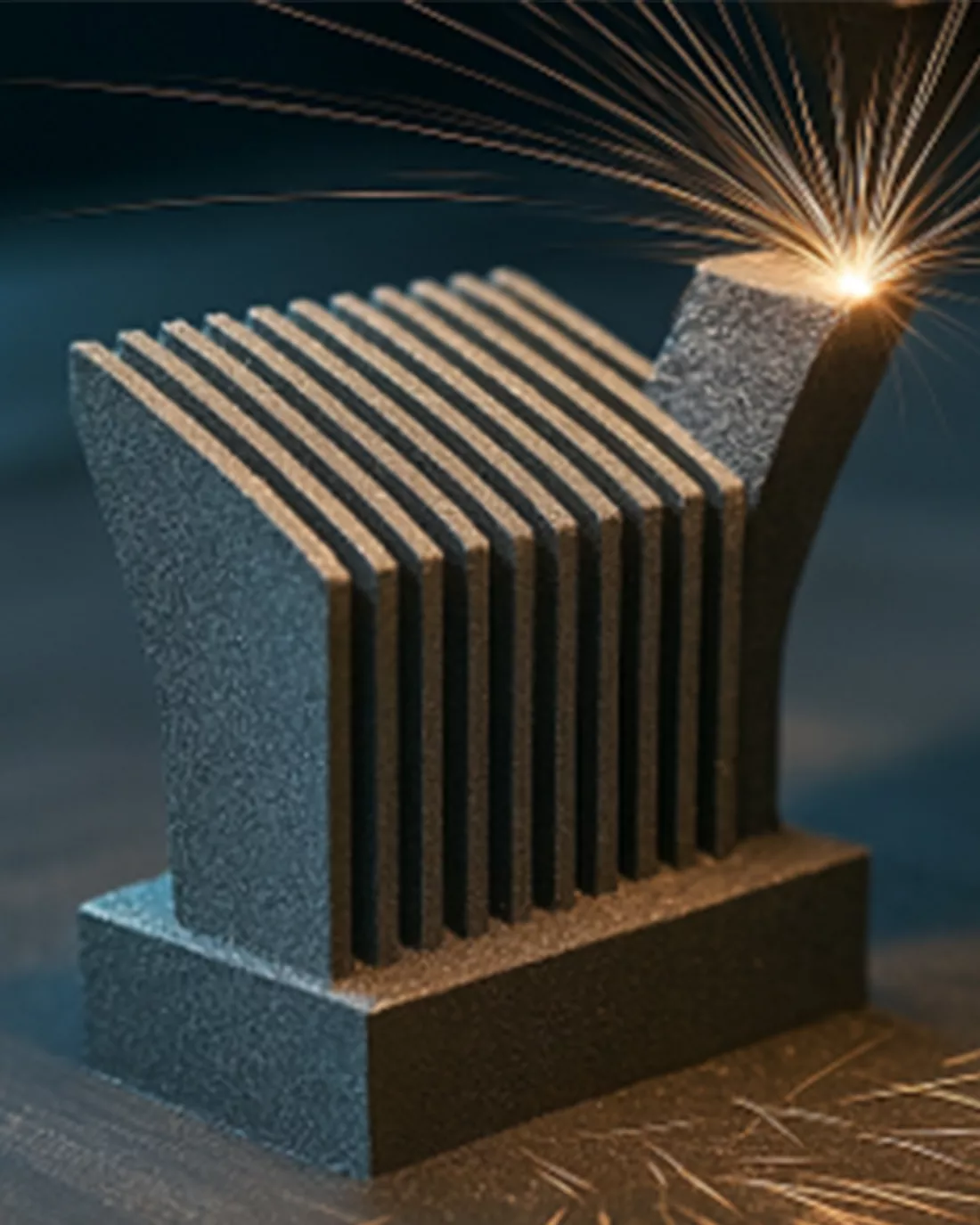
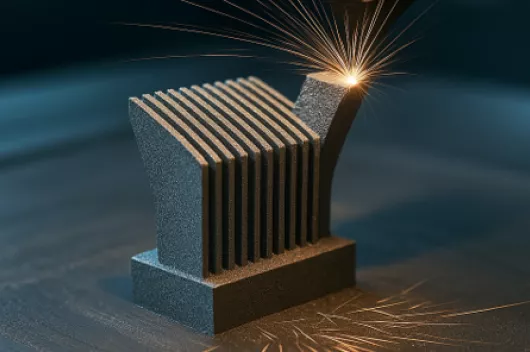
Synchrotron CT for Defects Analysis of Additively Manufactured Materials
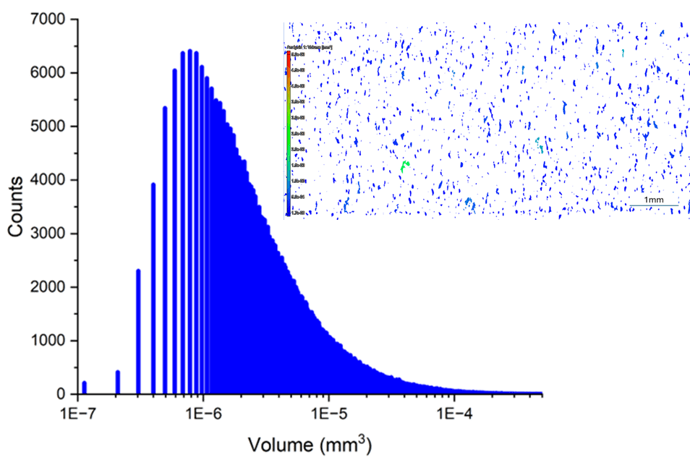
Our imaging expertise enables us to detect defects such as cracks or pores in additively manufactured materials . Using high-resolution synchrotron computed tomography (CT), we can gain detailed insights into the shape and size distribution of the defects. This method provides an exact three-dimensional representation of the defects and where they are located, allowing weak points to be precisely located and analyzed.
Porosity Analysis using Synchrotron CT data
Neutron Diffraction for Studying Residual Stresses in Materials
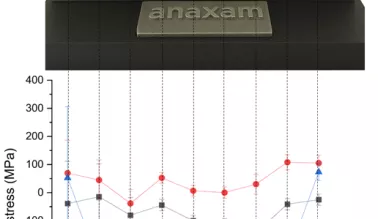
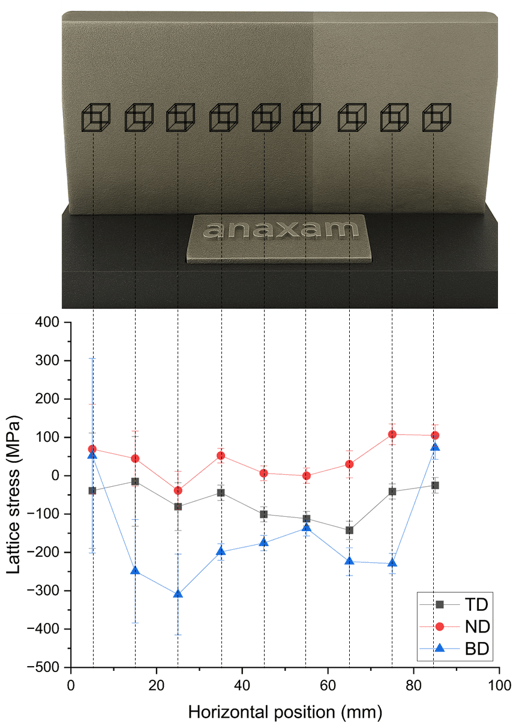
Our expertise in the area of diffraction allows us to measure residual stresses in materials. With residual stress analysis using neutron diffraction we study the changes of the residual stresses inside an engineering part nondestructively. This is useful especially for additive manufactured parts where residual stresses are hardly unavoidable due to the thermal cycles during the process.
Residual Stress Analysis
These customers trust our expertise
















































































Success stories

Lincotek Additive has been working on improvements in the AM process for some 15 years, drawing on the expertise of a team with a deep understanding of metallurgy, additive processing and design. Reactive metals, such as titanium, produce specific challenges, and high-temperature heat treatments involve a great deal of complexity. Lincotek Additive is mastering these challenges, resulting in best-in-class scrap rates and high reliability in our production processes.
By using the advanced analytics of ANAXAM, Lincotek Additive gets a deeper insight and understanding about SLM-processed high temperature materials.”

CondenZero was founded 2019 as a spin-off company of the Laboratory for Quantum Matter Research of the University of Zurich in Switzerland. Our field of expertise includes the development and production of scientific instruments and components for research applications in ultra-high vacuum and cryogenic conditions.
Additive manufacturing (AM) is a key process in our production chain and vacuum leak tightness of our components is essential. Thanks to ANAXAM state-of-the-art analytical tools were utilized to investigate the properties and microstructure of our AM parts regarding leak tightness.”
Let’s discuss your challenge
Answers to the most frequently asked questions
Neutron diffraction is a powerful technique for measuring residual stresses in additive-manufactured (AM) parts. It provides non-destructive, bulk stress analysis by penetrating deep into the material. Whether neutron diffraction is a suitable method depends on the material composition, part size, and crystal structure. Here’s a breakdown of the types of AM parts suitable for neutron diffraction residual stress analysis:
1. Material Types
- Metals and Alloys: Neutron diffraction works best with crystalline materials. Common AM metals suitable for analysis include:
- Stainless steels (e.g., 316L)
- Titanium alloys (e.g., Ti-6Al-4V)
- Nickel-based superalloys (e.g., Inconel 718) - Ceramics: Some ceramic parts with a crystalline structure can also be measured.
- Composites: Metallic matrix composites with distinct phases can be analyzed
2. Additive Manufacturing Techniques
- Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF): Common in aerospace and medical applications—typically prone to residual stresses due to rapid thermal cycling.
- Electron Beam Melting (EBM): Suitable for high-temperature materials like titanium alloys, which can exhibit internal stresses.
- Directed Energy Deposition (DED): Useful for large-scale components; neutron diffraction can reveal stress gradients across builds.
3. Geometrical Considerations
- Part Size: Neutron diffraction can penetrate several centimeters (5–30 mm) into most metals, making it suitable for bulkier components.
- Complex Geometries: With precise alignments, Stresses in intricate or internal geometries can be analyzed
4. Practical Considerations
- Grain Structure: Fine-grained structures give better diffraction signals. Coarse-grained materials may need texture correction.
- Resolution: Depends on the measured gauge volume.
Residual stress can be measured using neutron diffraction because neutrons, being deeply penetrating, allow for non-destructive measurements of stresses inside a material.
Residual stress affects the spacing between atomic planes (called the d-spacing) in a crystalline material. Neutron diffraction measures these spacings using Bragg's Law:
nλ=2dsinθ
- λ: Wavelength of the incident neutron beam
- d: Interplanar spacing
- θ: Bragg angle (measured during the experiment)
- If there's stress in the material, it changes d, which in turn shifts θ. Measuring this shift lets you calculate the strain and then stress.
- Deep Penetration into Materials
- Non-Destructive
- 3D Stress Analysis
- Direct measurement, no sample preparation required
- Suitable for Complex Geometries
- Applicable to a Wide Range of Materials
Additive manufacturing (like selective laser melting or electron beam melting) builds parts layer by layer, involving rapid heating and cooling. This causes:
- High thermal gradients
- Complex residual stress fields throughout the part
Learn more about us
The large-scale research facilities for our applied material analytics with neutron and synchrotron radiation
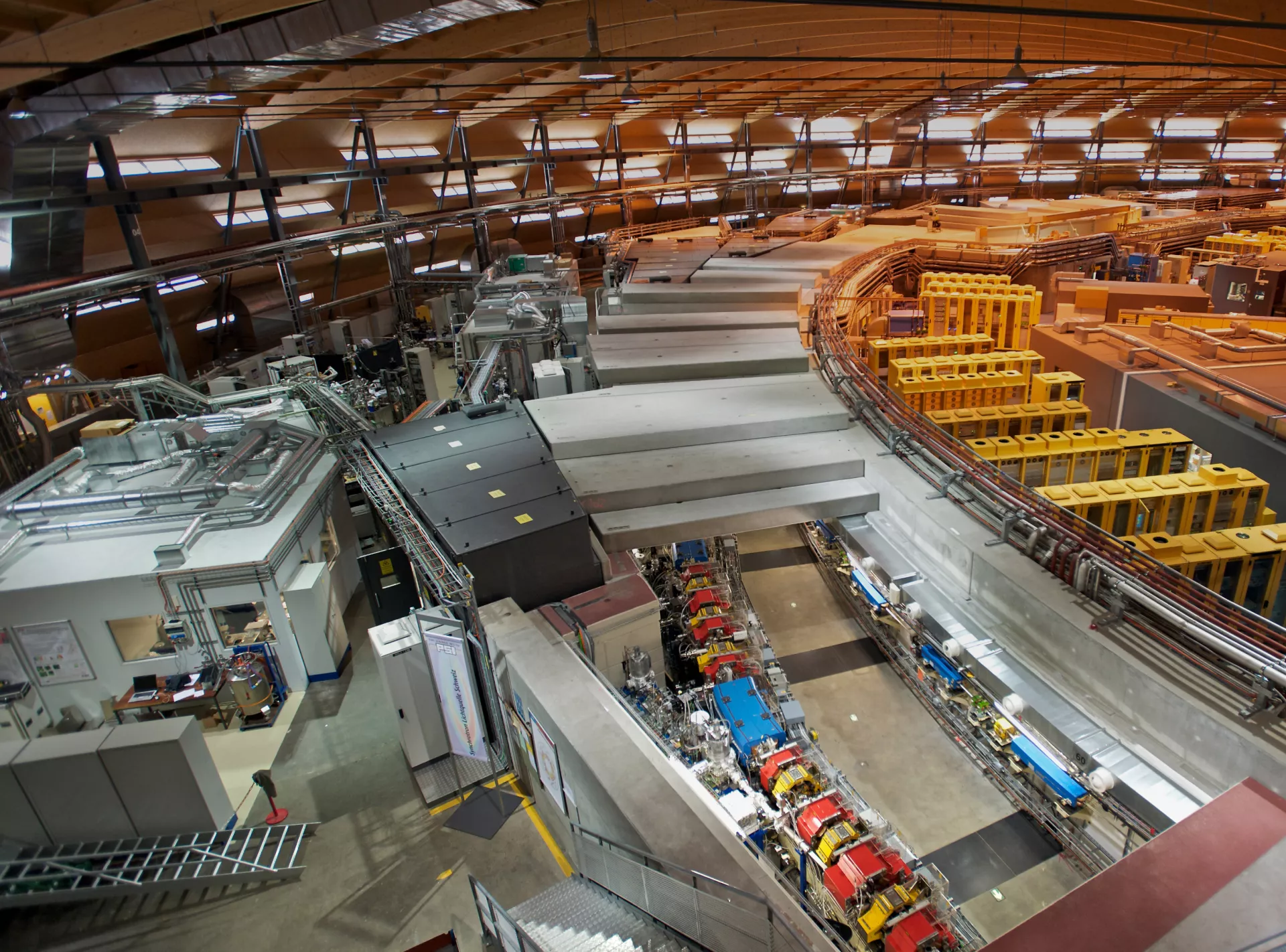
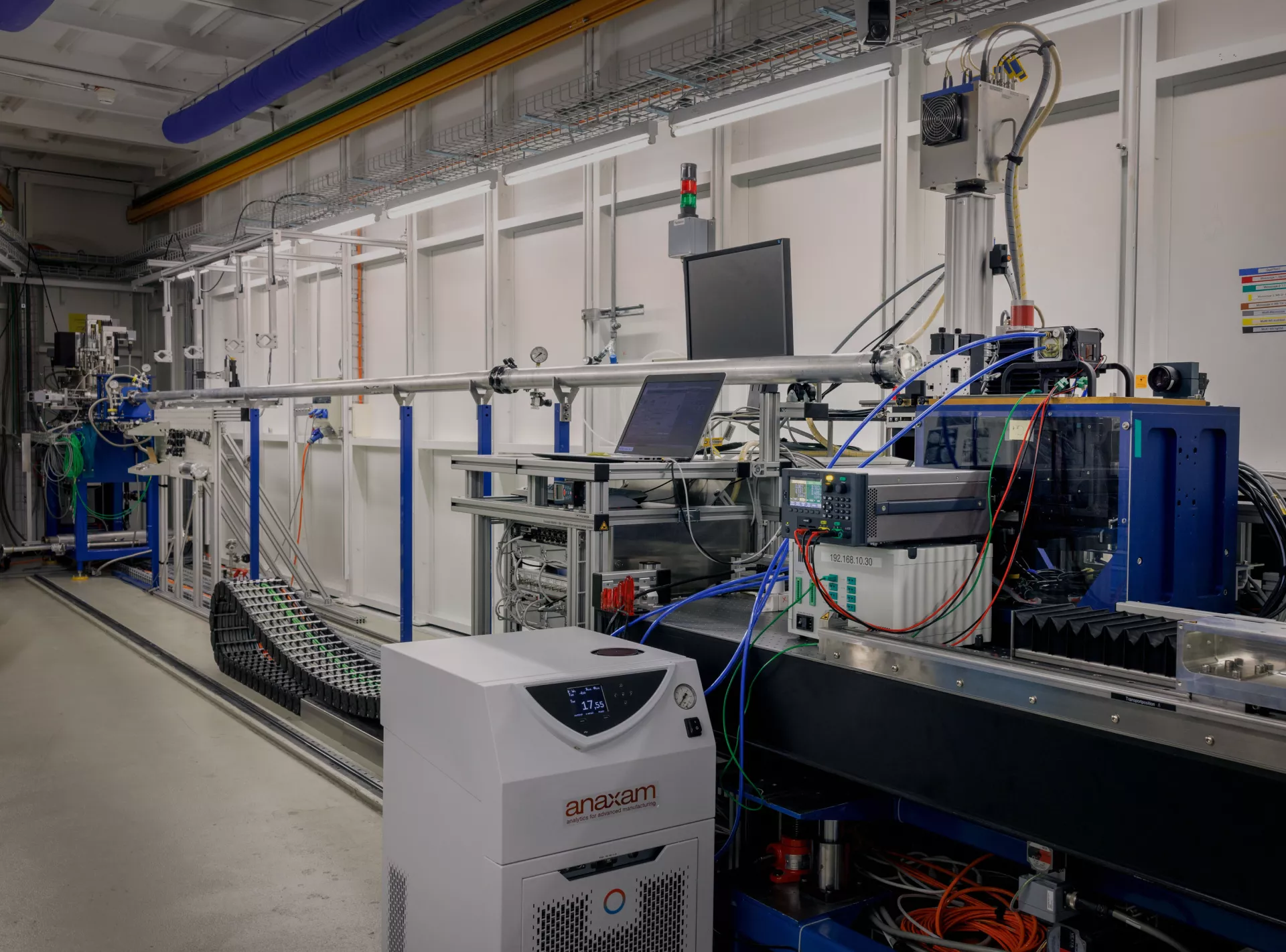
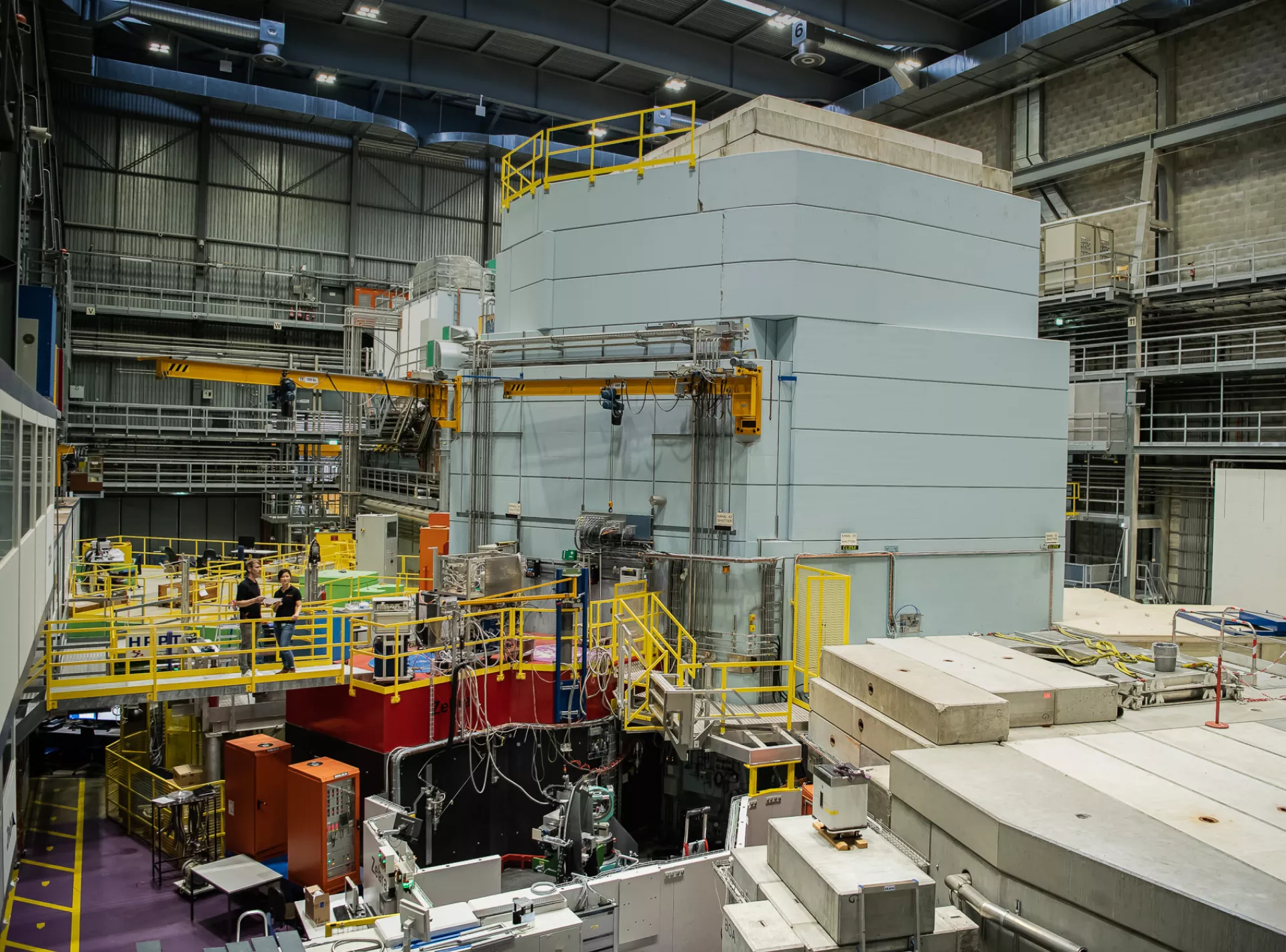
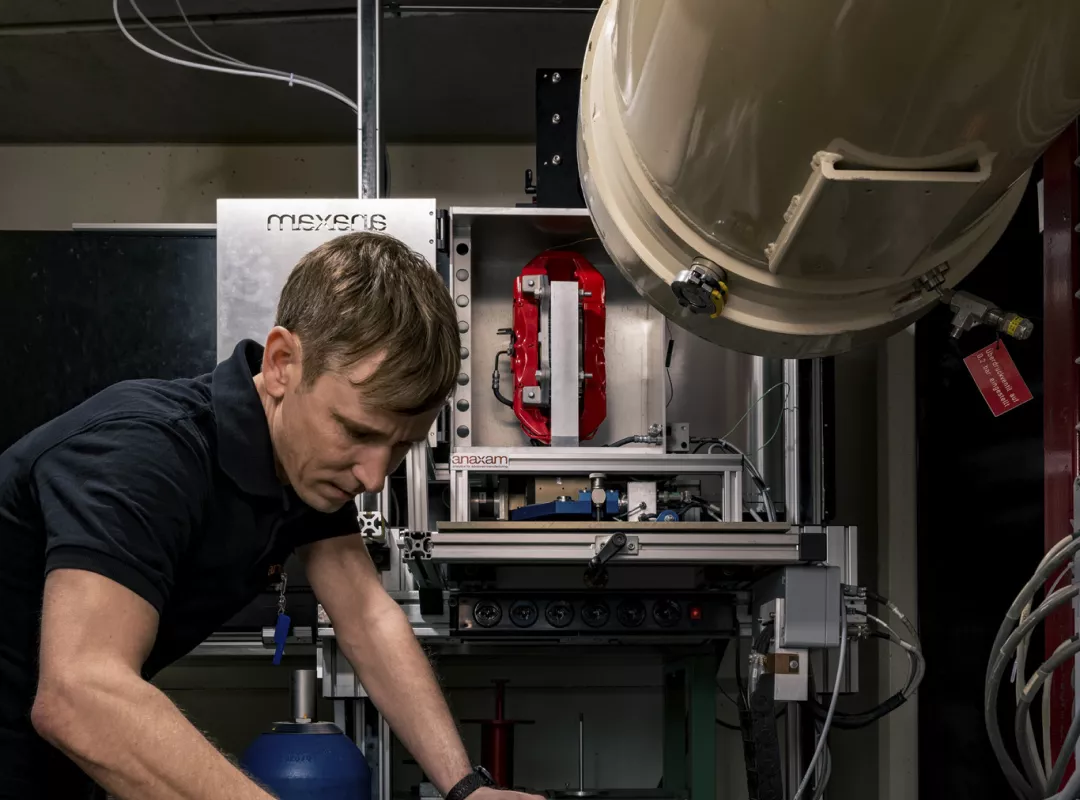
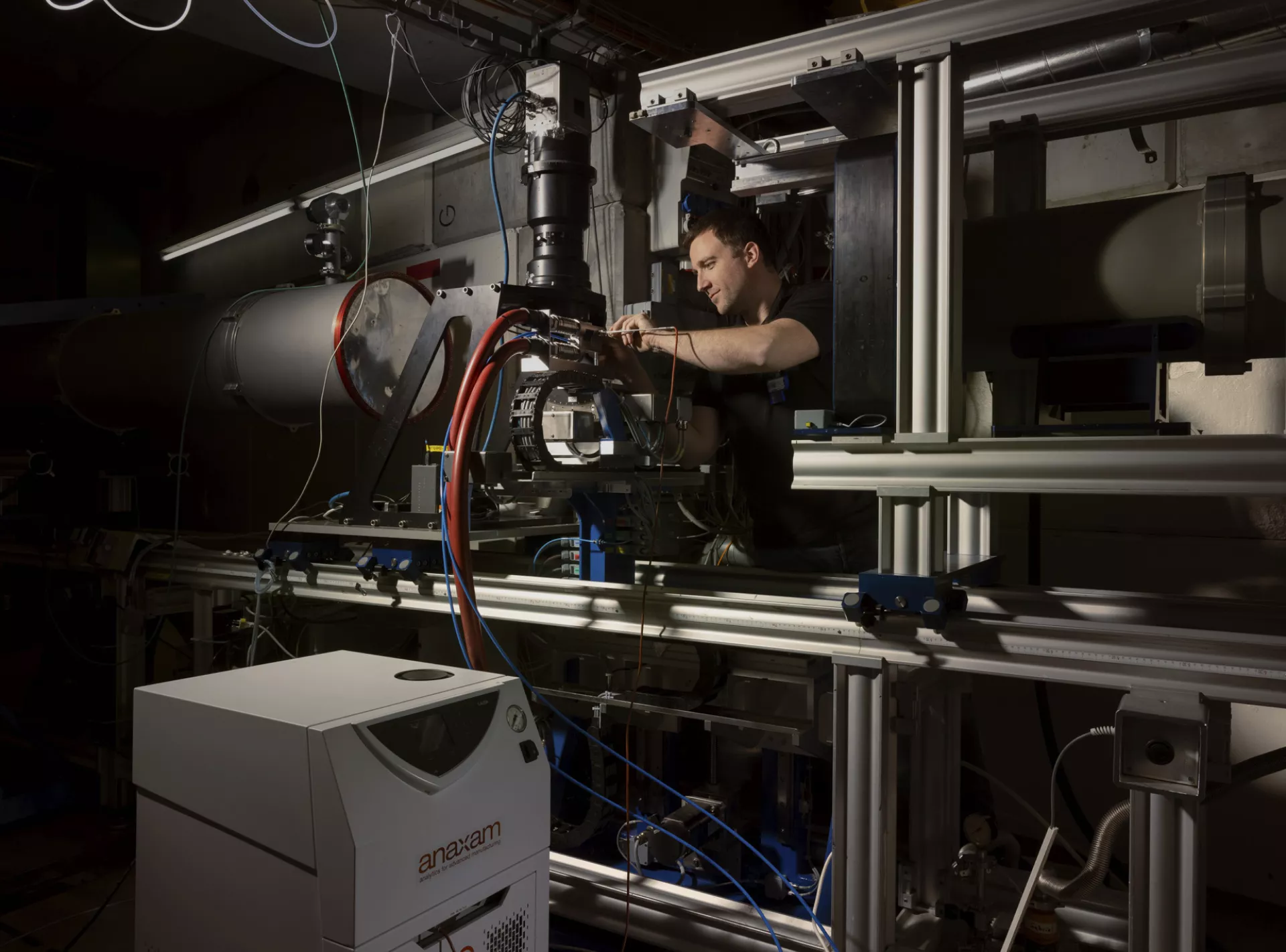









Tippen Sie auf die Pins, um sie zu erkunden
Die Art und Weise, wie wir mit Ihnen zusammenarbeiten
Ihre
Herausforderung
Kompetente
Beratung
Angewandte Materialanalytik mit Neutronen- und Synchrotronstrahlung &
massgeschneiderter Infrastruktur
Datenanalyse und
Interpretation
Abschliessender
Bericht